A trade union known as a Labour union or Workers Union is a group of workers who come together to protect and advocate for their rights and interests within a particular industry or workplace.
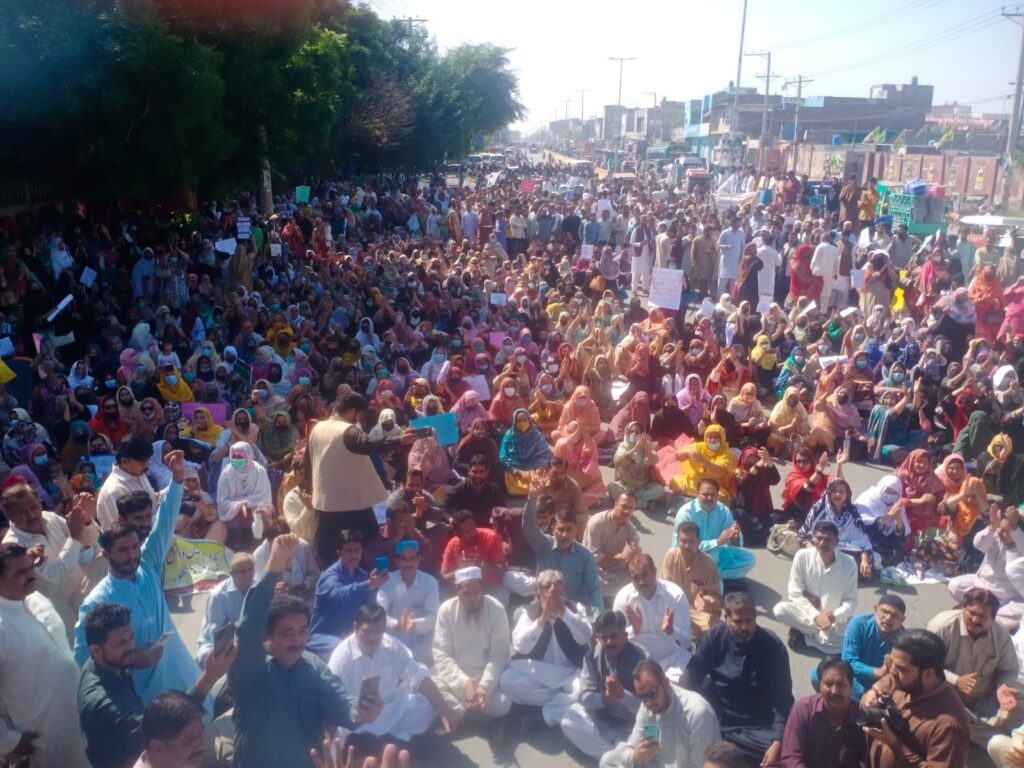

Relevant Laws For Forming a Trade Union, Join A Labour Union and Running Union Activities In Pakistan:
The Constitution of the Islamic Republic of Pakistan guarantees the right to form associations and unions under Article 17.
Right to Form Unions: Article 17 explicitly grants every citizen of Pakistan the right to form associations or unions. This provision is crucial for workers as it places the legal foundation for establishing trade unions, allowing them to come together to advocate for their collective interests.
Collective Bargaining: By enabling the formation of trade unions, Article 17 facilitates collective bargaining, which is essential for negotiating better wages, working conditions, and other employment-related issues with the employer.
Industrial Relations Act, 2012: This act brings together laws regarding the formation of trade unions and the management of industrial relations. It allows workers to form and join trade unions without needing prior approval, thereby safeguarding their right to engage in collective bargaining.
The National Industrial Relations Commission -NIRC is a key institution in Pakistan established to oversee and facilitate industrial relations, particularly in the context of trade unions and labour disputes.
The NIRC is responsible for registering trade unions and federations issuing approvals of the election and ensuring that they operate within the legal framework established by the Industrial Relations Act 2012.
Provincial Industrial Relations Acts or Labour Laws: Following the 18th Constitutional Amendment In Pakistan, labour matters became a provincial subject, resulting in the enactment of specific laws in each province.
The Khyber Pakhtunkhwa Industrial Relations Act, 2010 (KPIRA) is a provincial law in Pakistan that regulates labour relations, trade unions, and collective bargaining within the Khyber Pakhtunkhwa province. It defines key terms such as “collective bargaining agent”, “establishment”, “industrial dispute”, and “industry”.
The Punjab Industrial Relations Act, 2010 (PIRA) is a legislative framework that governs labour relations, trade unions, and collective bargaining in the Punjab province of Pakistan.
The Sindh Industrial Relations Act, 2013 (SIRA) is a regulatory framework that governs labour relations, trade unions, and collective bargaining in the Sindh province of Pakistan. It applies to all persons employed in various sectors, including agriculture and fishing while excluding certain categories such as civil servants and military personnel.
The Balochistan Industrial Relations Act, 2022 (BIRA) establishes a legal framework for labour relations, promoting the formation of trade unions and collective bargaining within the province. The law applies to all workers and employers in Balochistan, with specific provisions for addressing industrial disputes and ensuring workers’ rights.
How Trade Unions Protect Workers Rights:
Collective Bargaining
Trade unions provide workers with a collective voice to negotiate better wages, benefits, and working conditions with employers, management and the Government. By coming together, workers have more power to advocate for their rights and needs.

Trade unions strive to ensure that labour laws and regulations are properly enforced in workplaces. They keep an eye on compliance with minimum wage, overtime pay, workplace safety, and other legal requirements.
Safeguarding Worker Rights:
Occupational Health and Safety OSH:
Trade unions work towards enhancing occupational health and safety standards in workplaces. They can push for better safety and personnel Protective Safety equipment, training, and accident prevention measures from employers or management.
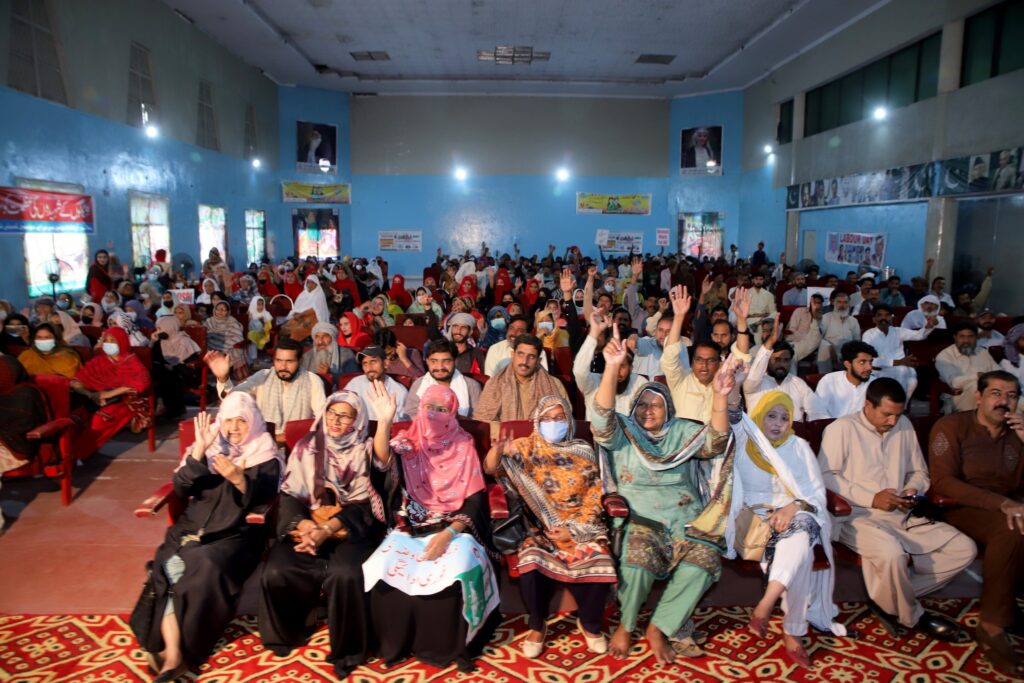

Empowering Women Workers:
Trade unions play a significant role in empowering women workers by raising awareness about their rights, offering leadership opportunities, and tackling gender discrimination issues by promoting democratic practices.
The trade unions are crucial for workers in Pakistan to collectively assert their rights, enhance their working conditions, and ensure a fair and equitable relationship with employers. However, the Labour union movement in Pakistan faces challenges such as fragmentation, lack of resources, and under-representation of women, which need to be addressed.

Challanges For The Workers:
As Pakistan battles with economic instability, rising inflation and precarious employment, the situation of workers has become worse than ever. The Pakistani workers c face a multitude of challenges, from irregular wages to poor working conditions, from insecurity to welfare benefits. Amidst these growing concerns, the role of organizations has never been more important. Trade unions in Pakistan are a major force in defending workers’ rights, providing a platform for collective bargaining and ensuring that workers’ voices are heard and respected.

The economic landscape in Pakistan is damaged by inflation rates that continue to skyrocket, making it increasingly difficult for workers to make ends meet. Basic commodities have become luxuries for many, and the gap between wages and the cost of living is opening up at an alarming rate. Moreover, the lack of adequate labour laws and enforcement has left workers vulnerable to exploitation and abuse, with many toiling in unsafe conditions without the security of a fair wage or social protection.
.Trade unions in Pakistan are a major force in defending workers’ rights, providing a platform for collective bargaining and ensuring that workers’ voices are heard and respected.